Hello again, this is Shusei Tomonaga from the Analysis Center. Event log analysis is a key element in security incident investigation. If a network is managed by Active Directory (hereafter, AD), can be identified by analysing AD event logs. For such investigation, it is quite difficult to conduct detailed analysis in AD event viewer; it is rather common to export the logs to text format or import them into SIEM/log...
List of “朝長 秀誠 (Shusei Tomonaga)”
-
-
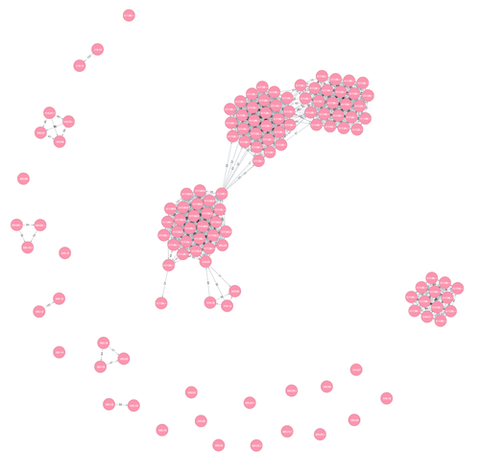
In a past article, we introduced “impfuzzy for Neo4j”, a tool to visualise results of malware clustering (developed by JPCERT/CC). In this article, we will show the result of clustering Emdivi using the tool. Emdivi had been seen until around 2015 in targeted attacks against Japanese organisations. For more information about Emdivi, please refer to JPCERT/CC’s report. Clustering Emdivi with impfuzzy for Neo4j Emdivi has two major variants - t17...
-
JPCERT/CC has been seeing a number of APT intrusions where attackers compromise a host with malware then moving laterally inside network in order to steal confidential information. For lateral movement, attackers use tools downloaded on infected hosts and Windows commands. In incident investigation, traces of tool and command executions are examined through logs. For an effective incident investigation, a reference about logs recorded upon tool and command executions would be...
-
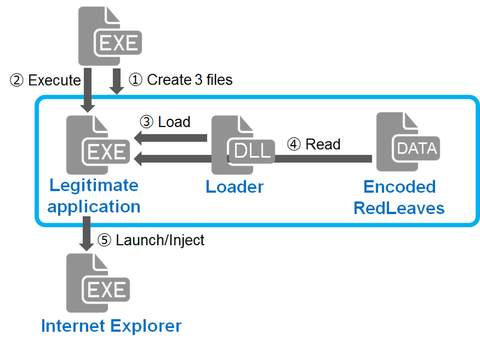
Our previous blog entry introduced details of RedLeaves, a type of malware used for targeted attacks. Since then, we’ve seen reports including those from US-CERT that Management Service Providers (MSPs) have been targeted [1] [2]. In the US-CERT report, some instances have been identified where RedLeaves malware has only been found within memory with no on-disk evidence because of the behavior of self-elimination after the infection. To verify the infection...
-
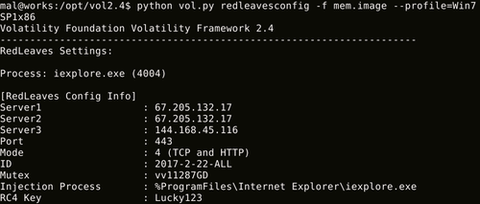
Hi again, this is Shusei Tomonaga from the Analysis Center. Since around October 2016, JPCERT/CC has been confirming information leakage and other damages caused by malware ‘RedLeaves’. It is a new type of malware which has been observed since 2016 in attachments to targeted emails. This entry introduces details of RedLeaves and results of our analysis including its relation to PlugX, and a tool which is used as the base...
-
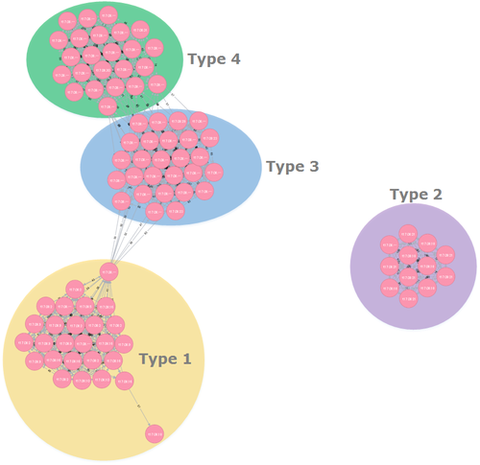
Hi again, this is Shusei Tomonaga from the Analysis Center. This entry introduces a malware clustering tool “impfuzzy for Neo4j” developed by JPCERT/CC. Overview of impfuzzy for Neo4j impfuzzy for Neo4j is a tool to visualise results of malware clustering using a graph database, Neo4j. A graph database is a database for handling data structure comprised of records (nodes) and relations among the records. Neo4j provides functions to visualise registered...
-
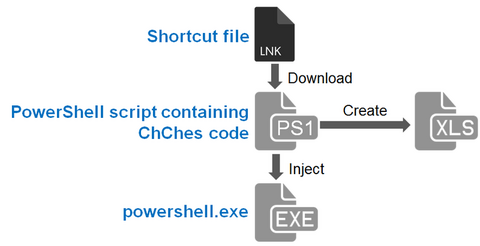
Hi again, this is Shusei Tomonaga from the Analysis Center. In this article, I’d like to share some of our findings about ChChes (which we introduced in a previous article) that it leverages PowerSploit [1] – an open source tool – for infection. Flow of ChChes Infection The samples that JPCERT/CC confirmed this time infect machines by leveraging shortcut files. The flow of events from a victim opening the shortcut...
-
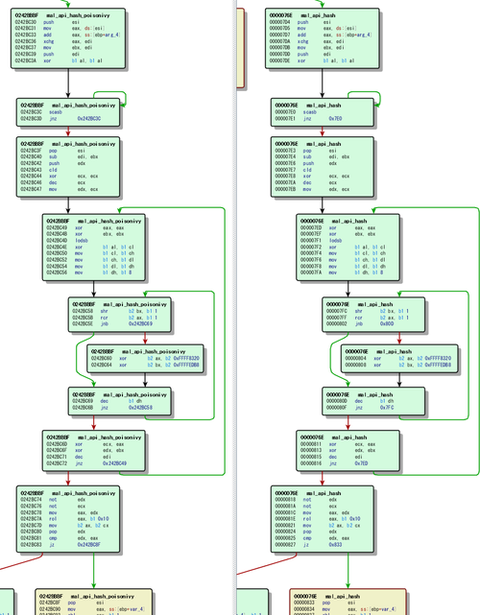
Hi again, this is Shusei Tomonaga from the Analysis Center. PlugX is a type of malware used for targeted attacks. We have introduced its new features in the blog article “Analysis of a Recent PlugX Variant - ‘P2P PlugX‘”. This article will discuss the following two structural changes observed in PlugX since April 2016: the way API is called the format of main module changed from PE to raw binary...
-
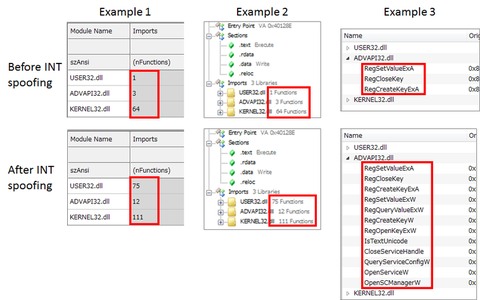
When analysing Windows executable file type (PE file) malware, a tool to parse and display the PE file’s structure (hereafter “PE analysis tool”) is often used. This tool enables referring to a list of APIs that the malware imports (Import API) and functions that it exports. By analysing the data, it is possible to presume the malware’s function as in communicating with external servers or creating registry entries, etc. In...
-
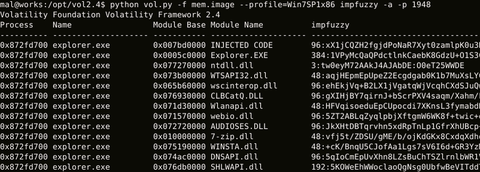
Hi again, this is Shusei Tomonaga from the Analysis Center. Today I will introduce a tool “impfuzzy for Volatility”, which JPCERT/CC has created for extracting known malware from memory images and utilises for analysis operations. Malware Detection in Memory Forensics To judge if a file type malware sample is a known kind, the easiest and fastest way is to check the hash value (e.g. MD5 or SHA 256) of the...